The boundaries of what's possible have expanded.
NEW
DYNAMIC DESIGN
LARGE FORMAT 3D PRINTER "KUZNETS"
NEW APPROACH TO 3D PRINTING
A new patented, dynamic design of the printer now does not constrain you to only working on flat surfaces that are in parallel to the printer's working plane. Therefore, there is no need for precision mechanisms or guides to navigate the printer head on the working bench. This allows us to create a 3D printer capable of printing large constructions at a competitive cost.
Another advantage of not being constrained to having the printer and surface in parallel is that we can offer printer models that can print on virtually any surface, thus reducing the costs for a large scale printer.
GREAT DESIGN
Minimalist design. Ideal for any interior. A lot of printing power packed into a small space makes it a great fit for your living space while allowing you to satisfy MANY 3D designs.
MINIMAL COST
The new dynamic design allows you to arrange all of the printer elements in the same plane with a sheet of tempered glass as the base. This approach allows us to reduce the cost of the printer by 30-40% relative to a standard 3D printer.
МОБИЛЬНОЕ ПРИЛОЖЕНИЕ
NEW
DYNAMIC
DESIGN
The 3D printer uses a new dynamic design.
The scheme allows you to position the 3D printer's actuators and linear guides within the same plane.
3D PRINTER DESIGN
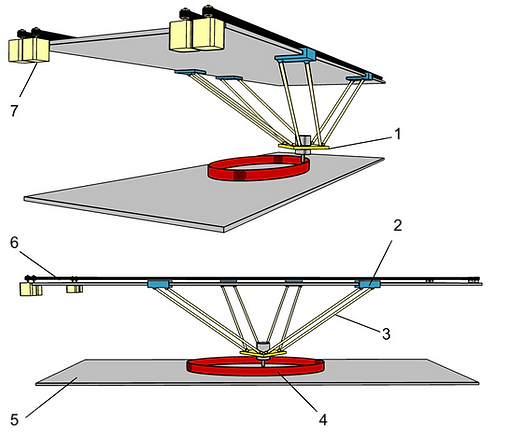

1. Printhead with hinges
2. Carriage with ball joints
3. Rod
4. Model
5. Desk
6. Toothed belt
7. Stepper motor
CAPABILITIES OF THE DESIGN
You can select the optimal height of the working surface before starting to print and fix it into place. This feature allows you to create 3D models of various sizes as the printing contraption has a flexible, voluminous shape.
The printing area can have a complex shape (seen below in blue):
Base area - 650 x 650 mm
Height - 360 mm
Volume - 0.14 m3
In comparison, the possible printing volume of a standard personal 3D printer is a 200 mm - sized cube.


COMPARISON WITH ANALAGOUS 3D PRINTERS
KUZNETS
BigRep ONE.2


3DP Unlimited X1000

Working volume (mm):
Layer resolution (micron):
Extruder:
Nozzle diameter:
Filament diameter:
Fabrication methods:
Printable materials:
Weight:
Size (mm):
Price:
x:650 y:650 z:350
100 – 1000
Dual nozzle
0.4 mm
1.75 mm
FFF (FDM)
PLA, CoPolymere, Laywood, Laybrick, ABS, PC, PA,
TPE, PVA, PS
15 kg
1800 x 500 x 150
$ 2 000 - 5 000
x:1100 y:1067 z:1097
100 – 1000
Dual nozzle
0.4 mm
3 mm
FFF (FDM)
PLA, CoPolymere, Laywood, Laybrick, ABS, PC, PA,
TPE, PVA, PS
410 kg
1800 x 1700 x 1990
$39 999
х: 1000 y: 1000 z: 500
70 - 100
Dual nozzle
0.4 mm
3 mm
FFF (FDM)
PLA, ABS, PC, Nylon, Ninja Flex, PVA, HIPS
120 kg
1422 x 1358 x 990
$16 699
FROM THEORY TO APPLICATION
-
BUILT PROTOTYPE
-
FILED PATENT APPLICATIONS
-
SOFTWARE UNDER DEVELOPMENT
МОБИЛЬНОЕ ПРИЛОЖЕНИЕ
NEXT STEPS FOR DEVELOPING THE DYNAMIC DESIGN
PHASE 1
This printer is already fully suitable for companies involved in 3D printing, as it allows you to make products with large dimensions, has the ability to scale, is compact and is cheap.
We plan to expand the functionality of the printer in the near future. It will be possible to combine several printers to print a single, larger item that will allow much more flexible and more efficient use of the printers for the customer . You can see our plans on the page Future 1
PHASE 2
The emergence of new technologies in video-analytics and 3D-scanning opens up new doors to create interactive technology to build physical 3D-models (filed a patent).
Today's 3D printers build the physical model "blindly," i.e. without feedback and control over the result. This limits you to three-dimensional rigid structures with precise models where the dimensions of the model are determined by the dimensions of the 3D printer.
The interactive process of constructing a physical 3D model is done in several stages: the printer scans the already-constructed part of the physical model, compares it with the digital model, and completes the missing layers within the operating range of the printing head stroke. Afterwards, it moves either the model or printer to scan the model, and continues to build.
Our concepts for interactive printing technology can be found on the page Future 2